Building Technologies:
Plywood

What is it?
Plywood is a composite material that is made out of layers of wood laid in opposition to one another. By laying the wood out like this, the load can be bore on any side of the composite. Therefore, the material can be customized and worked with accordingly.

How it works:
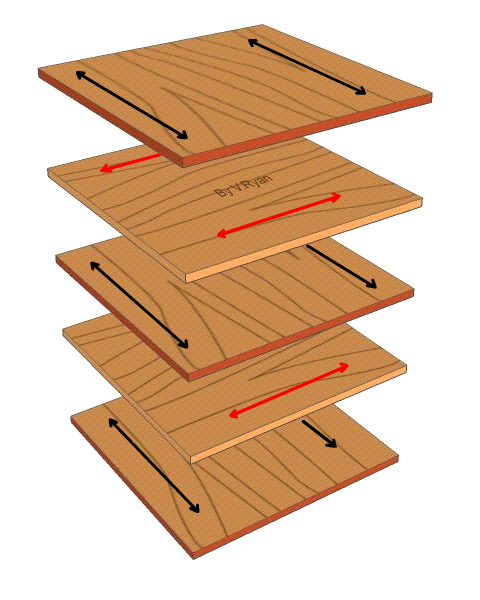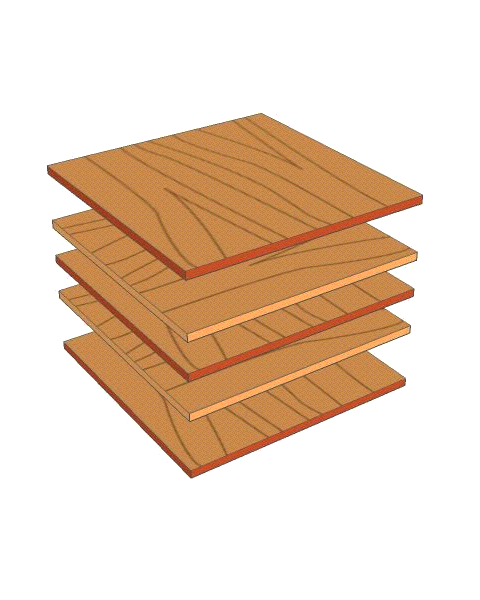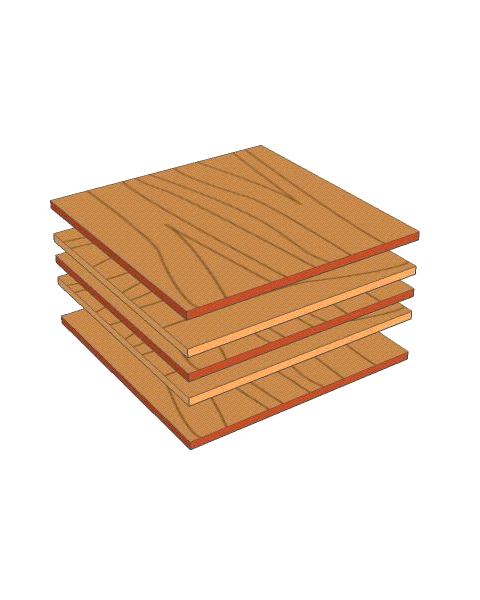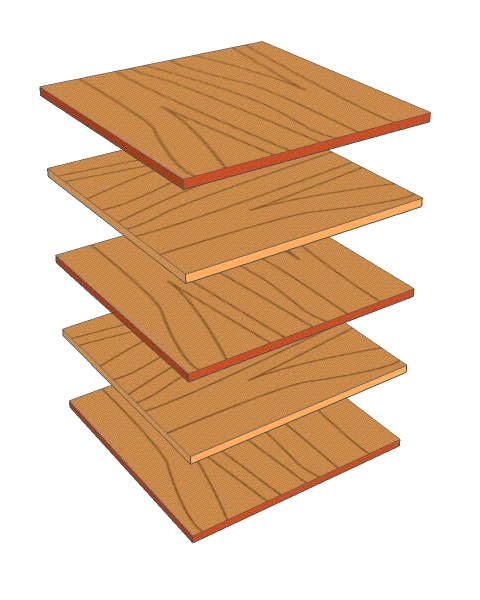
Plywood's ability to multiply the vectors in which stress can travel down a wood grain's interior is it's primary strength as a building material. This keeps it lightweight despite it's ability to carry significant loads given the former.
Aesthetic ramifications
Plywoods' unique aesthetic benefits cannot be realized without understanding its construction process. It seeks to tame an otherwise streamlined and narrow use-case of wood in timber building and give it new dimensions (literally).
The material can do this by generalizing the grain, and therefore the direction implied by the growth patterns of the wood. When used in great sheets - the wood seeks to be an organic monolith other than stick-built building - which opens up many interesting use cases.

Plywood can be used in tandem with traditional wood architecture to create a layering effect. The monolithicism in the wood is apparent in both it's massing presence and it's color apart from the lumber format.
The textures and hues that plywood provides depends, as other types of wood - on the species and treatment process. In this apartment in London, plywood as a finish is used despite not being part of the construction. The pine species used for it imparts knots, which present a different texture and therefore atmosphere.


Plywood is a material that beckons for other materials. In this house plywood is left as a finish but does occur with other elements such as a ceramic backsplash. This is an inversion of its monolithicism - and uses it as more of a piecewise design detail.
Questions for further reading
To what extent do the different glues used in plywood affect the strength given the costs. What are the different types, at that?
...aka things to consider
How does the strength of the plywood given the unit mass square up with heavier-duty engineered wood, such as Cross-Laminated Timber and Glulam?
Were there any analogues to plywood in history? There are ancient varieties of concrete, masonry, and - of course - timber.